Contents page
Our society has physical assets that have a tangible and perceivable form. These include real estate, consumer goods (cars or clothes), and natural resources (gold or oil).
On the other hand, we have digital assets, which are inherently intangible and digital. This means they do not exist physically in the real world. We create, store, and exchange them electronically. An example of this would be an eBook.
In the context of blockchain, these digital assets are called tokens. A token is a specific type of digital asset. Its characterized by being coded, stored, and exchanged on an existing blockchain such as Ethereum, Solana, or Binance Smart Chain.
The image below illustrates this concept, with physical assets on the left and tokens (digital assets anchored on the blockchain) on the right.

Characteristics of a token
Fungible vs non-fungible token
A token can be divided into two categories : fungible or non-fungible, as shown in the image above.
In the case of fungible tokens, commonly referred to simply as tokens, each token is identical and interchangeable. Standards such as ERC-20 generally govern these tokens for a token created on the Ethereum platform. These standards ensure their uniformity across blockchain networks.
For example, bitcoin is a fungible token. Indeed, one Bitcoin (BTC) can be exchanged for another bitcoin without losing value or functionality. As shown in the image below, just as one dollar is interchangeable with another dollar, one bitcoin is also interchangeable with another bitcoin.

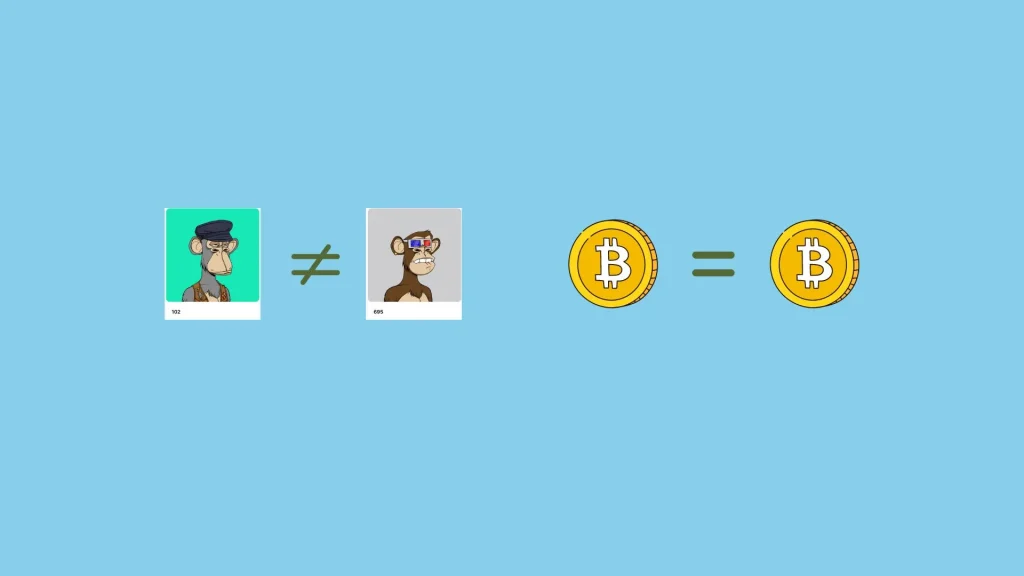
In the case of non-fungible tokens, commonly referred to as NFTs, each token is unique and possesses different features. These tokens are created according to standards such as ERC-721 on the Ethereum blockchain. This ensures their uniqueness across blockchain networks. Consequently, a non-fungible token cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis.
For example, non-fungible token No. 102 from the Bored Ape Yacht Club collection does not have the same characteristics as No. 695, making it unique. As shown in the image below, each NFT in the Bored Ape Yacht Club collection is unique, much like a Pokémon card.

Other characteristics of a token
Tokens have specific characteristics that distinguish them from other digital assets. These characteristics include :
- Managed by smart contracts: Tokens are created and managed by smart contracts. These automatically execute the rules encoded for these tokens, including their transfer management, reward distribution, or the execution of certain functions without intermediaries.
- Issued by private entities: These digital assets are often issued by private companies.
- Representation of value: A token represents a unit of value, typically embodying a form of ownership or access right.
- Diverse uses: Tokens can have various uses, determined from their conception. These uses depend on the goal of the blockchain project that issues them.
Different categories of tokens
Although tokens can be categorized into two types, fungible or non-fungible as seen earlier, they can also be classified into two major categories : utility tokens and security tokens.
Utility tokens
Utility tokens are designed to provide access to an application or service within a blockchain ecosystem. They can be used to pay for services, offer discounts, grant voting rights, or provide access to specific features or exclusive services on platforms.
These tokens facilitate the creation of a viable economic model that encourages active use and participation in the project.
It is important to note that a utility token does not confer ownership rights over the company or project. However, it allows users to interact with the platforms.
Example of utility token :
- BNB : The cryptocurrency exchange platform Binance issued BNB. BNB allows users to pay for goods and services, generate passive income, pay transaction fees on the Binance Smart Chain, obtain cryptocurrency loans, and participate in exclusive token sales. By using BNB, users benefit from a 25% discount on spot and margin trading fees, as well as a 10% discount on futures trading fees.
We can classify utility tokens into several subcategories, includinggovernance tokens (e.g., UNI from Uniswap) or stablecoins (e.g., USDT from Tether).
Security tokens
Security tokens are similar to traditional stocks and can represent an investment in a company, often granting rights to dividends or profit shares.
Example of security token :
- tZERO : tZERO tokens represent an equity stake in the tZERO platform. Holders are entitled to a share of tZERO’s profits, similar to preferred shares in a traditional company.
Financial authorities such as the SEC in the United States or the AMF in France strictly regulate security tokens. They impose rigorous disclosure, compliance, and registration requirements to protect investors.
🔎 Explore the economic models of many tokens available on Tokenomics Data
The importance of tokens in blockchain projects and their tokenomics models
Tokens play a central role in the blockchain ecosystem, offering a multitude of features and benefits. By facilitating digital transactions, providing economic incentive mechanisms, and enabling decentralized governance, they pave the way for new forms of interaction, funding, and governance. Thus, tokens contribute to the creation of viable, sustainable, and participatory economic models. They also allow for efficient and transparent value distribution, fostering financial innovation and investment accessibility.
In the context of tokenomics, tokens are essential components for structuring, stimulating, and regulating the economic activities of blockchain projects.